
Structures Found In Prokaryotic And Eukaryotic CellsĪll living organisms use cellular organization to create structures to conduct life processes. Both types of cells have vacuoles, storage units for food and liquid.Amoebas, paramecia, and yeast are all single-cell eukaryotes. Both prokaryotes and eukaryotes may be single-celled organisms.Both prokaryotic cells and eukaryotic cells have vesicles.Both cells carry DNA and rDNA (ribosomal DNA).However, they do these things in different ways. Both types of cells carry on all the necessary functions of life (adaptation through evolution, cellular organization, growth and development, heredity, homeostasis, reproduction, metabolism, and response to stimuli).Similarities Between Prokaryotic And Eukaryotic Cellsįor all their differences, prokaryotes and eukaryotes have a few similarities share some common structures (due to physics and evolution), and though their DNA is different, they even share some genetic features.īoth types of cells have five similarities: Prokaryotic cells have circular strands of DNA eukaryotic cells have multiple molecules of double-stranded, linear DNA.Prokaryotic cells have no organelles enclosed in plasma membranes every eukaryotic cell has a nucleus and organelles, each enclosed in plasma membranes.Prokaryotic cells have no mitochondria nearly every eukaryotic cell has mitochondria.
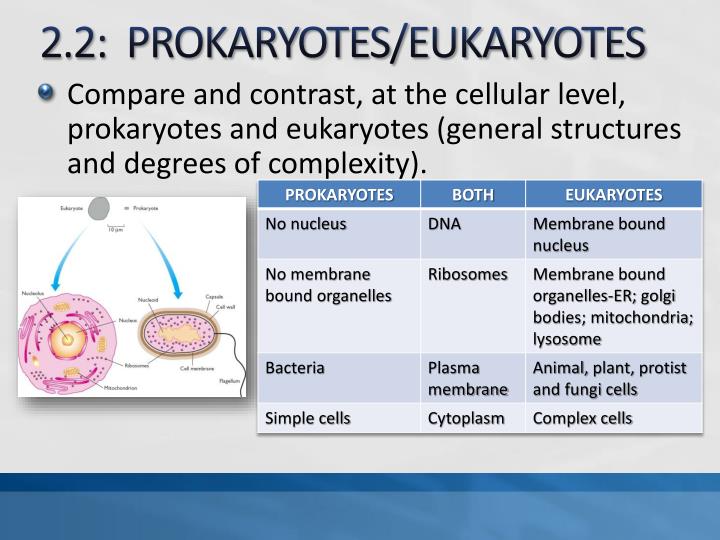
No prokaryotic cell has a nucleus every eukaryotic cell has a nucleus.The most obvious difference between them is that prokaryotes have no nuclei, but there are four major differences between a eukaryotic and prokaryotic cell: Difference Between Eukaryotic And Prokaryotic Cells


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
